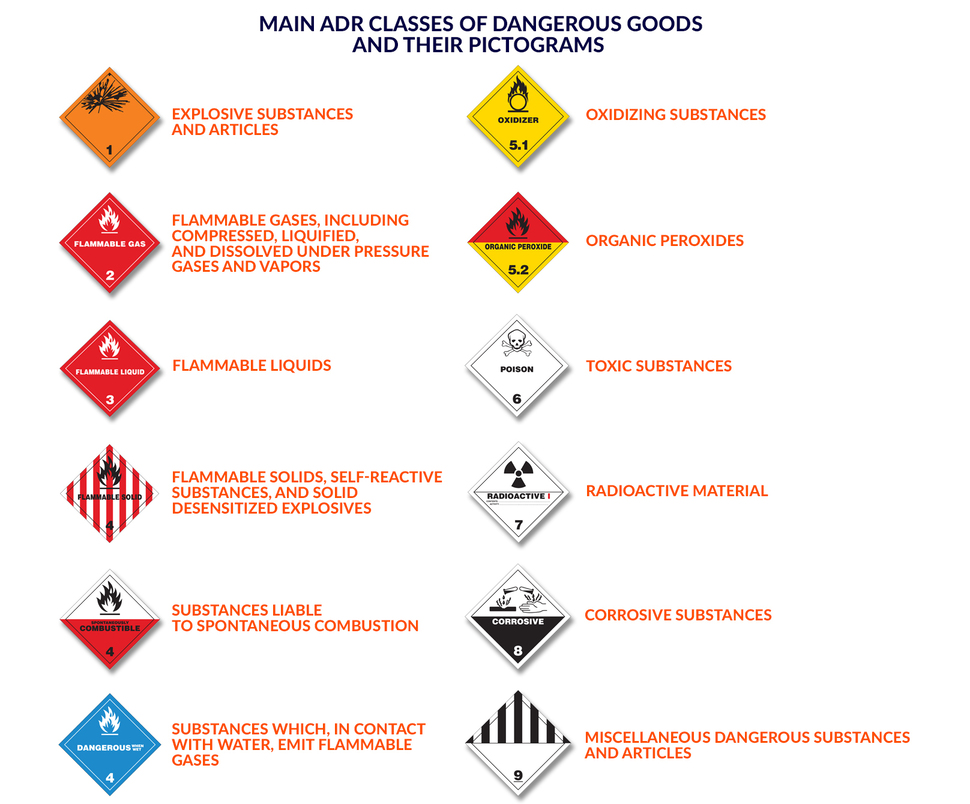
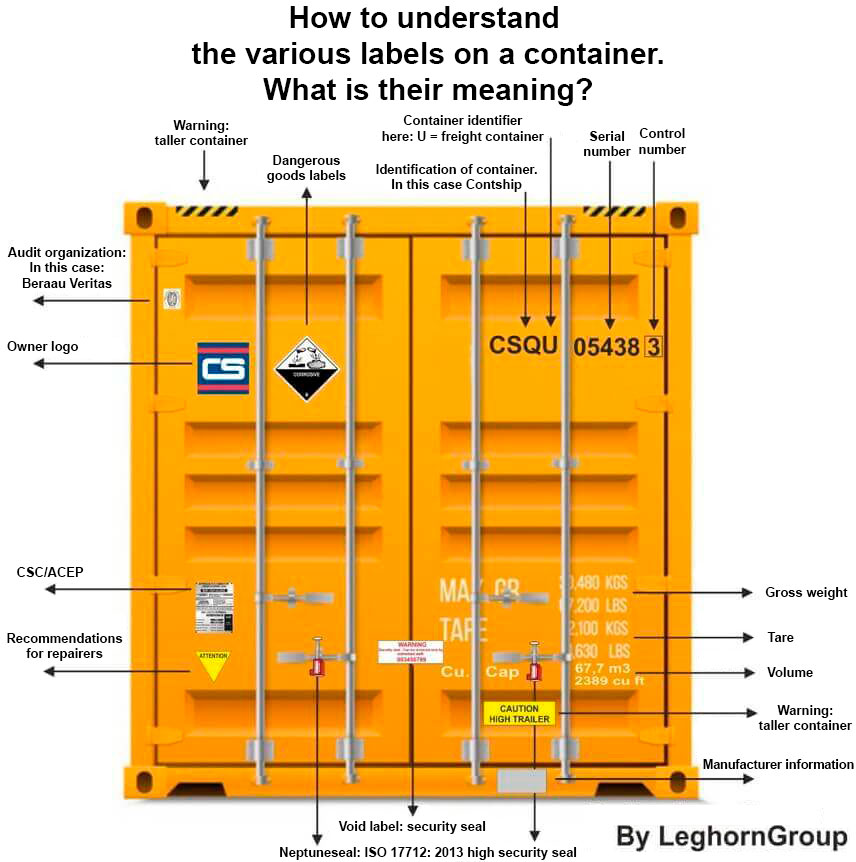
44 adr labels for dangerous goods
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › ADR_(treaty)ADR (treaty) - Wikipedia ADR, formally the Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road is a 1957 United Nations treaty that governs transnational transport of hazardous materials. "ADR" is derived from the French name for the treaty: Accord relatif au transport international des marchandises Dangereuses par Route). unece.org › transport › dangerous-goodsDangerous Goods | UNECE Nov 19, 2021 · ADR provisions are the result of more than 50 years of best practices in the transport of dangerous goods on roads. A revised edition of ADR including these amendments (ADR 2023) is in press and is expected in Autumn 2022. Printed versions and electronic editable versions will be available for sale at the United Nations Publications section.
Linguistic versions (ADR, Instructions in writing) | UNECE ADR 2001 (files) Labels (GHS) Protocol(s) amending ADR. Protocol amending the title of the European Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) Protocol of 1993 amending Article 1(a), Article 14(1) and Article 14(3)(b) of the ADR; Protocol of signature; ADN. About the ADN; Status and ...
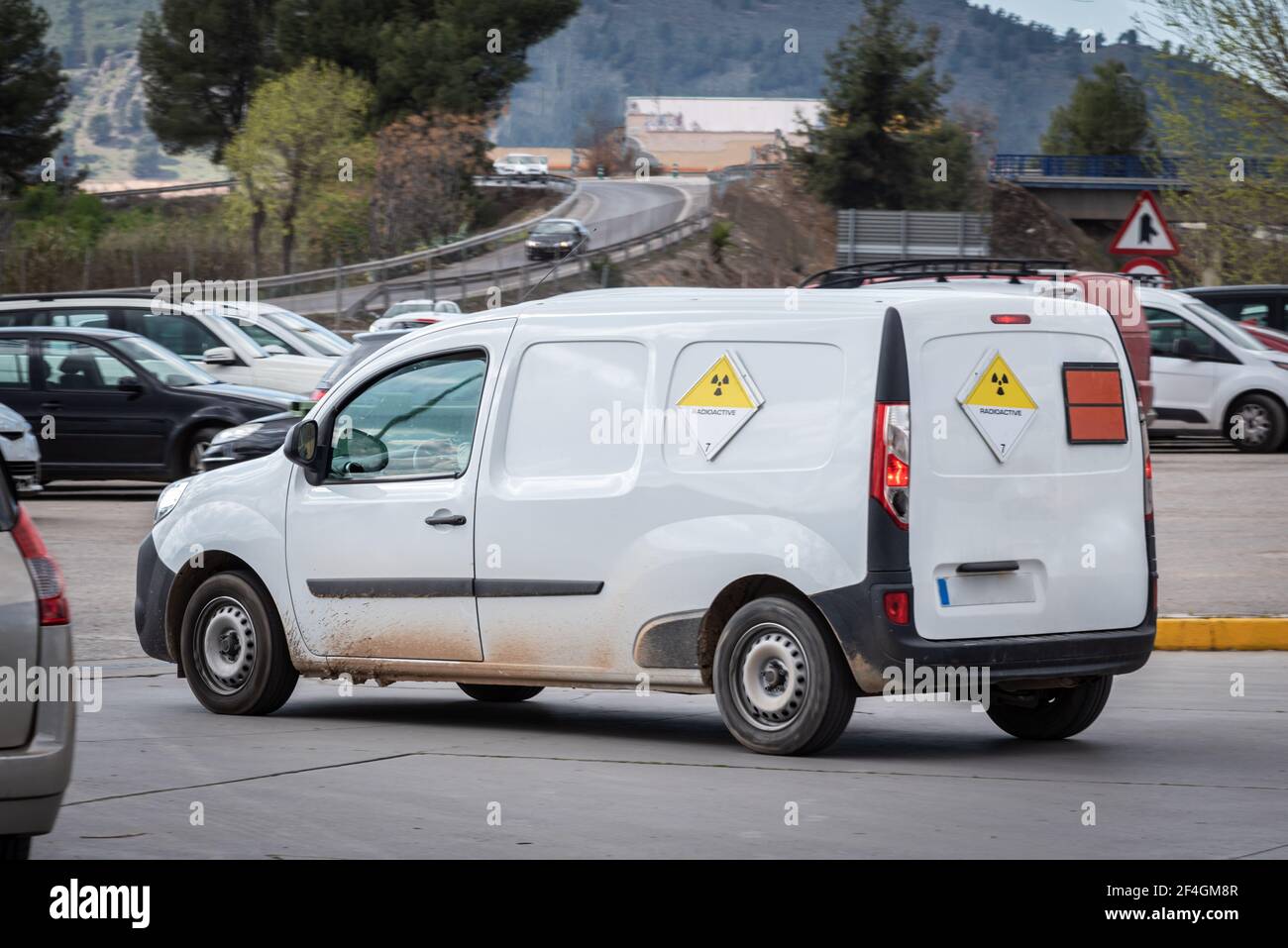

Adr labels for dangerous goods
ADR (treaty) - Wikipedia ADR, formally the Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road is a 1957 United Nations treaty that governs transnational transport of hazardous materials. "ADR" is derived from the French name for the treaty: Accord relatif au transport international des marchandises Dangereuses par Route). unece.org › transportdangerous-goods › adr-2017-filesADR 2017 (files) | UNECE Jan 01, 2017 · ADR 2009 (files) Amendments to ADR 2007; ADR 2007 (files) Amendments to ADR 2005; ADR 2005 (files) Amendments to ADR 2003; ADR 2003 (files) Amendments to ADR 2001; ADR 2001 (files) Labels (GHS) Protocol(s) amending ADR. Protocol amending the title of the European Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous ... adrdangerousgoods.com › eng › articlesClasses 1-9 of dangerous goods explained - ADR Dangerous Goods Jun 22, 2017 · If the goods have multiple dangerous propreties, the most dominant one determines the class to which it shall belong. The classes are part of the United Nations-based system of identifying dangerous goods, and are used within many different subsystems such as the ADR, RID, IMDG and DGR for classifying dangerous goods and hazardous materials.
Adr labels for dangerous goods. Carriage of dangerous goods: approved derogations and transitional ... 06.04.2020 · 1) For goods of Classes 2 to 6, 8 and 9: the documents required to be carried on the transport unit by ADR 8.1.2.1(a) need not be carried where the quantity of dangerous goods being carried on ... Dangerous Goods | UNECE 19.11.2021 · ADR 2001 (files) Labels (GHS) Protocol(s) amending ADR. Protocol amending the title of the European Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) Protocol of 1993 amending Article 1(a), Article 14(1) and Article 14(3)(b) of the ADR ; Protocol of signature; ADN. About the ADN; Status and … unece.org › about-adrAbout the ADR | UNECE Amendments adopted in 2020, 2021 and 2022 by the Working Party on the Transport of Dangerous Goods and contained in ECE/TRANS/WP.15/256 and Corrs 1-2 and ECE/TRANS/WP.15/256/Add.1 will enter into force on 1 January 2023. A revised edition of ADR including these amendments (ADR 2023) is in press and is expected in Autumn 2022. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Dangerous_goodsDangerous goods - Wikipedia Dangerous goods shipments also require a dangerous goods transport document prepared by the shipper. The information that is generally required includes the shipper's name and address; the consignee's name and address; descriptions of each of the dangerous goods, along with their quantity, classification, and packaging; and emergency contact ...
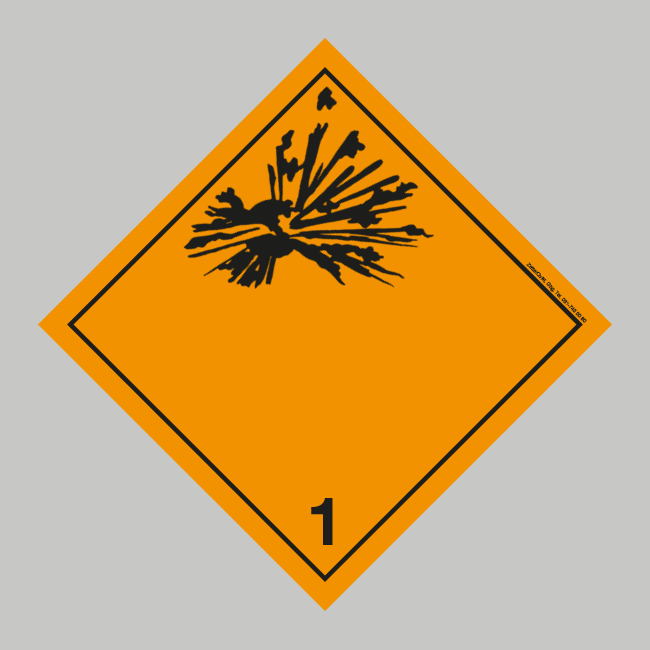
Classes 1-9 of dangerous goods explained - ADR Dangerous Goods 22.06.2017 · If the goods have multiple dangerous propreties, the most dominant one determines the class to which it shall belong. The classes are part of the United Nations-based system of identifying dangerous goods, and are used within many different subsystems such as the ADR, RID, IMDG and DGR for classifying dangerous goods and hazardous materials. Dangerous goods - Wikipedia Dangerous goods, abbreviated DG, are substances that when transported are a risk to health, safety, property or the environment.Certain dangerous goods that pose risks even when not being transported are known as hazardous materials (syllabically abbreviated as HAZMAT or hazmat).An example for dangerous goods is hazardous waste which is waste that has … About the ADR | UNECE ADR 2001 (files) Labels (GHS) Protocol(s) amending ADR. Protocol amending the title of the European Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) Protocol of 1993 amending Article 1(a), Article 14(1) and Article 14(3)(b) of the ADR; Protocol of signature; ADN. About the ADN; Status and ... ADR 2019 (files) | UNECE 01.01.2019 · ADR 2001 (files) Labels (GHS) Protocol(s) amending ADR. Protocol amending the title of the European Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) Protocol of 1993 amending Article 1(a), Article 14(1) and Article 14(3)(b) of the ADR; Protocol of signature; ADN. About the ADN; Status and …
unece.org › fr › about-adrAbout the ADR | UNECE ADR 2001 (files) Labels (GHS) Protocol(s) amending ADR. Protocol amending the title of the European Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) Protocol of 1993 amending Article 1(a), Article 14(1) and Article 14(3)(b) of the ADR; Protocol of signature; ADN. About the ADN; Status and ... ADR 2017 (files) | UNECE 01.01.2017 · ADR 2001 (files) Labels (GHS) Protocol(s) amending ADR. Protocol amending the title of the European Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) Protocol of 1993 amending Article 1(a), Article 14(1) and Article 14(3)(b) of the ADR ; Protocol of signature; ADN. About the ADN; Status and … About the ADR | UNECE The Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road (ADR) was done at Geneva on 30 September 1957 under the auspices of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe, and it entered into force on 29 January 1968. The Agreement itself was amended by the Protocol amending article 14 (3) done at New York on 21 August 1975, which … adrdangerousgoods.com › eng › articlesClasses 1-9 of dangerous goods explained - ADR Dangerous Goods Jun 22, 2017 · If the goods have multiple dangerous propreties, the most dominant one determines the class to which it shall belong. The classes are part of the United Nations-based system of identifying dangerous goods, and are used within many different subsystems such as the ADR, RID, IMDG and DGR for classifying dangerous goods and hazardous materials.
unece.org › transportdangerous-goods › adr-2017-filesADR 2017 (files) | UNECE Jan 01, 2017 · ADR 2009 (files) Amendments to ADR 2007; ADR 2007 (files) Amendments to ADR 2005; ADR 2005 (files) Amendments to ADR 2003; ADR 2003 (files) Amendments to ADR 2001; ADR 2001 (files) Labels (GHS) Protocol(s) amending ADR. Protocol amending the title of the European Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous ...
ADR (treaty) - Wikipedia ADR, formally the Agreement of 30 September 1957 concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road is a 1957 United Nations treaty that governs transnational transport of hazardous materials. "ADR" is derived from the French name for the treaty: Accord relatif au transport international des marchandises Dangereuses par Route).

































Post a Comment for "44 adr labels for dangerous goods"